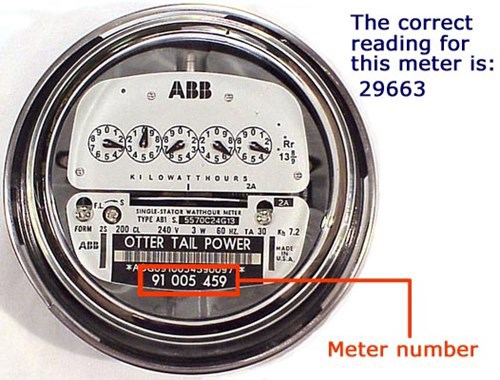
Some electric meters have multiple dials, each with a pointer and the numerals 0 to 9. Below is an example of a five-dial electric meter. Notice that the pointers on the first, third, and fifth dials move clockwise. The second and fourth pointers move counter clockwise.

Here's how to read a dial meter:
- Stand directly in front of the meter so that you clearly can see the location of each pointer.
- If the pointer is between two numbers, read the lower number.
- If the pointer is between 9 and 0, read 9.
- If the pointer appears to be exactly on a number, read the next lower number unless the pointer on the dial to your right has passed zero. You must read the dial on the far right independently.
- Each meter is numbered. Note your meter number.
Let's read this sample electric meter

- Start on the far right. The pointer on the far right is directly on 5. Read it as 5.
- The next pointer has just passed 9 and is between 9 and 0. Read it as 9.
- The next pointer has passed 8 and is between 8 and 9. Read the smaller number: 8.
- The pointer on the next dial is directly on the 4 but, because the dial to the right has not passed zero, read this dial as 3.
- The pointer on the far-left dial is between 8 and 9. Read the smaller number: 8.
|
Current reading |
83895 |
|
Minus last reading |
- 83770 |
|
Electricity use |
= 125 |
|
The difference of 125 kilowatt-hours is the amount of electricity used since the last reading. |
|
Some meters have a constant or multiplier, which is shown on the nameplate. If so, the reading on the meter may be 1/40 or 1/10 of the energy used. In this case, to determine actual use multiply the electricity used by this constant.